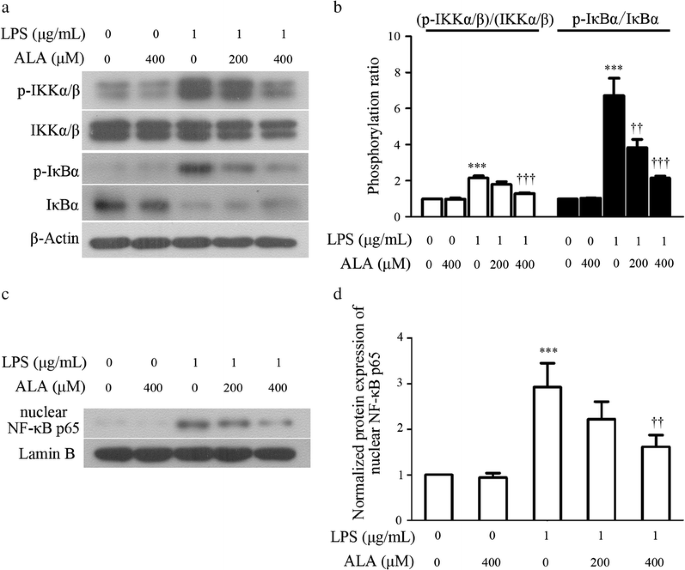
Alpha-Lipoic Acid Exerts Anti-Inflammatory Effects on Lipopolysaccharide-Stimulated Rat Mesangial Cells via Inhibition of Nuclear Factor Kappa B (NF-κB) Signaling Pathway | SpringerLink

Protective Effect of α-Lipoic Acid in Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Endothelial Fractalkine Expression | Circulation Research

Alpha-lipoic acid effectively attenuates ionizing radiation-mediated testicular dysfunction in rats: Crosstalk of NF-ĸB, TGF-β, and PPAR-ϒ pathways - ScienceDirect

Encapsulation and Stabilization of α-Lipoic Acid in Cyclodextrin Inclusion Complex Electrospun Nanofibers: Antioxidant and Fast-Dissolving α-Lipoic Acid/Cyclodextrin Nanofibrous Webs | Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry

Regeneration of glutathione by α-lipoic acid via Nrf2/ARE signaling pathway alleviates cadmium-induced HepG2 cell toxicity - ScienceDirect

NF-κB activation as a pathological mechanism of septic shock and inflammation | American Journal of Physiology-Lung Cellular and Molecular Physiology

Alpha‐lipoic acid: A possible pharmacological agent for treating dry eye disease and retinopathy in diabetes - Ajith - 2020 - Clinical and Experimental Pharmacology and Physiology - Wiley Online Library

α-Lipoic Acid, an Organosulfur Biomolecule a Novel Therapeutic Agent for Neurodegenerative Disorders: An Mechanistic Perspective | SpringerLink

NF-κB activation as a pathological mechanism of septic shock and inflammation | American Journal of Physiology-Lung Cellular and Molecular Physiology

Alpha-lipoic acid (ALA) supplementation effect on glycemic and inflammatory biomarkers: A Systematic Review and meta- analysis - Clinical Nutrition ESPEN

Inhibition of NF-κB Activation by Pyrrolidine Dithiocarbamate Prevents In Vivo Expression of Proinflammatory Genes | Circulation

α-Lipoic Acid Potentiates the Anti-Inflammatory Activity of Avocado/Soybean Unsaponifiables in Chondrocyte Cultures - Carmelita G. Frondoza, Lowella V. Fortuno, Mark W. Grzanna, Stacy L. Ownby, Angela Y. Au, Ann M. Rashmir-Raven, 2018

Figure describing the role of α-LA as anti-oxidant, anti-inflammatory,... | Download Scientific Diagram
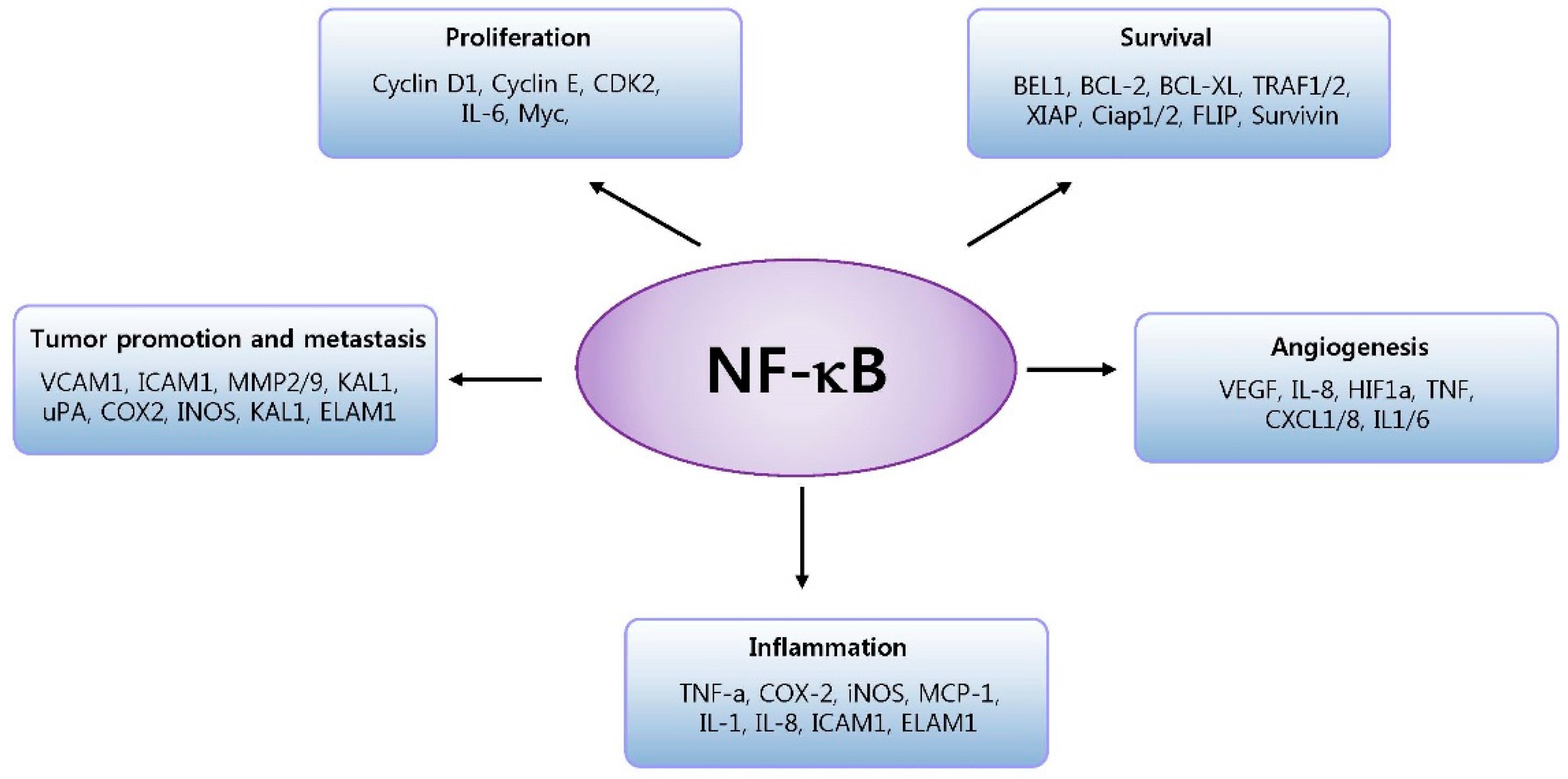
Cells | Free Full-Text | Roles of NF-κB in Cancer and Inflammatory Diseases and Their Therapeutic Approaches


:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/alpha-lipoic-acid-88727-primary-49db80751ca14a66ae8d162358080767.jpg)